Virtual Table
When you need to operate on multiple text data located under the same virtual control, Virtual Table Object (virtualTable) provides an efficient solution. Through the virtual table object, you can use it like operating a table.
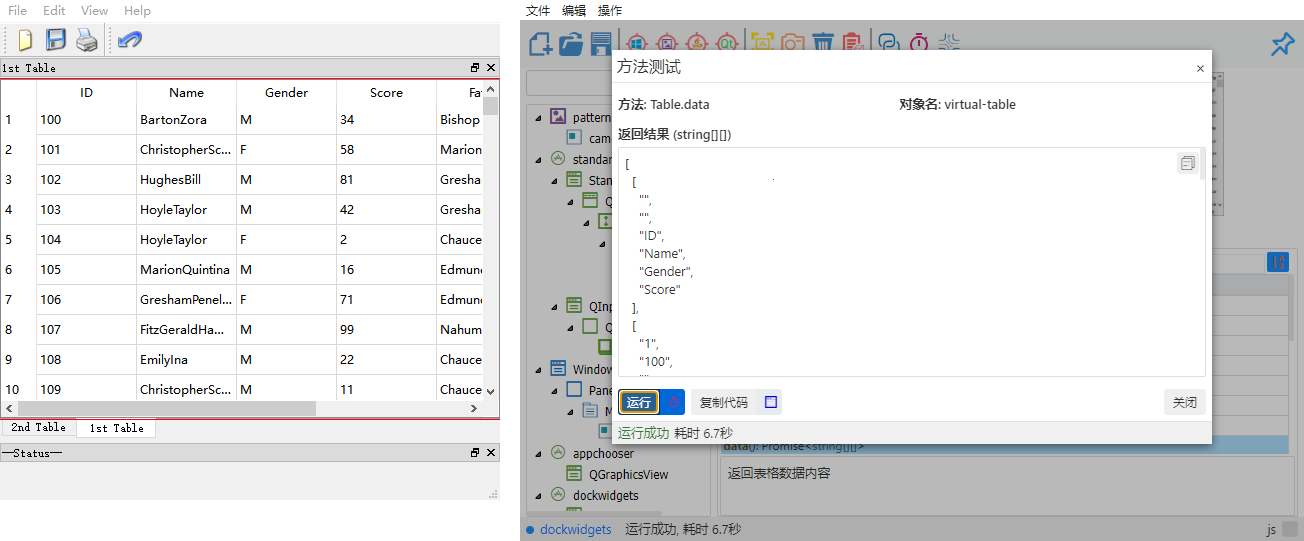
Add Virtual Table Object
After creating a virtual control in the Model Manager, find the object properties tab, click Add Property, add objectType property, select Table as the property value, and click Add to successfully add it.
You can also select the table icon and then click the checkmark icon after drawing the virtual control when creating it to complete the creation of the virtual table.
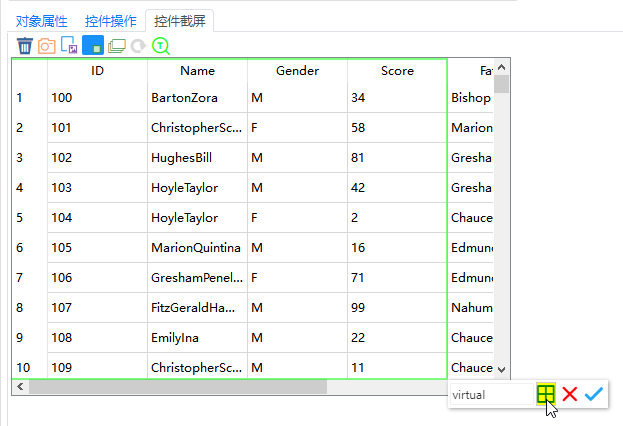
Return to the control operation tab to call the virtualTable related APIs.
In this way, you can avoid operating each text object individually, but access the required content directly by row and column. For example:
- Click a specific cell.
- Get the text content of a cell.
- Verify the correctness of cell text.
- Search and compare data in the table.
Usage Example
Suppose you are testing an application containing multiple contact information, where each contact's information (such as name, phone, email, etc.) is displayed in a list. By adding a text table object, you can easily verify the contact information of each row in the list, or find the information of a specific contact.
let virtualTable = await model.getVirtual("ContactsList");
let contactInfo = await virtualTable.cellValue(1, 2); // Get text of row 1, column 2 (assuming phone number)
console.log(`Contact Phone: ${contactInfo}`);
// Perform other text verification or operations...virtualTable = model.getVirtual("ContactsList")
contactInfo = virtualTable.cellValue(1, 2) # Get text of row 1, column 2 (assuming phone number)
print(f"Contact Phone: {contactInfo}")
# Perform other text verification or operations...Besides calling the virtual table directly by object name, you can also obtain the virtual table object and call related API methods through Descriptive Mode.
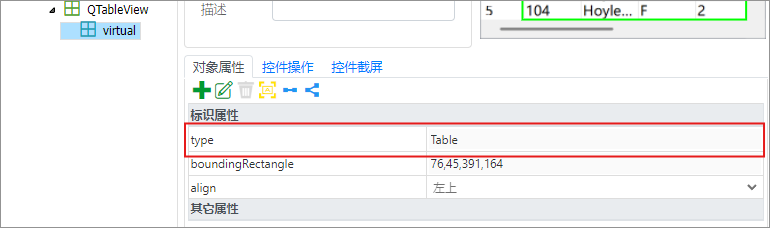
If you complete the creation of the virtual table object by clicking the table icon and then the checkmark icon after drawing the virtual control, you can see in Object Properties that the type property in the Identification Properties of the virtual table object is Table. This can be used as your object parameter when using Descriptive Mode.
Sample Code:
// Using descriptive mode requires getting the cascaded virtual table via the parent Table control
// After getting the virtual table object, use the data() method to get table data
let data = await model.getTable("table_name").getVirtual({"type": "Table"}).data();
console.log(data);# Using descriptive mode requires getting the cascaded virtual table via the parent Table control
# After getting the virtual table object, use the data() method to get table data
data = model.getTable("table_name").getVirtual({"type": "Table"}).data()
print(data)Virtual Table Object API
Type Definition
export interface Virtual {
clickCell(rowIndex: number, columnNameOrIndex: string | number): Promise<void>;
cellValue(rowIndex: number, columnNameOrIndex: string | number): Promise<string>;
columnName(index: number): Promise<string>;
columnHeaders(): Promise<string[]>;
columnCount(): Promise<number>;
data(): Promise<string[][]>;
rowCount(): Promise<number>;
rowData(rowIndex: number): Promise<string[]>;
}class Virtual(SyncBase):
def clickCell(rowIndex: int, columnNameOrIndex: Union[str, int]) -> None
def cellValue(rowIndex: int, columnNameOrIndex: Union[str, int]) -> str
def columnName(index: int) -> str
def columnHeaders() -> List[str]
def columnCount() -> int
def data() -> List[List[str]]
def rowCount() -> int
def rowData(rowIndex: int) -> List[str]Operation Methods
- clickCell(rowIndex: number, columnNameOrIndex: string | number)
- cellValue(rowIndex: number, columnNameOrIndex: string | number)
- columnName(index: number)
- columnHeaders()
- columnCount()
- data()
- rowCount()
- rowData(rowIndex: number)
data(): Promise<string[][]>
Get all content in the table and return it as a two-dimensional array.
- Return value:
Promise<string[][]>type, i.e., a two-dimensional string array.
Suppose the table data is as follows:
| ID | Name | Gender |
|---|---|---|
| 0001 | Alice | Male |
| 0002 | Bob | Male |
| 0003 | Cathy | Female |
Then the array returned by the data() method is as follows:
[
['0001', 'Alice', 'Male'],
['0002', 'Bob', 'Male'],
['0003', 'Cathy', 'Female']
]